Country research: Maldives
Homepage " Country research " Maldives
The content reflects the results of Perplexity's research and analysis and does not represent an expression of opinion by Gradido. They are intended to provide information and stimulate further discussion.
Maldives & Gradido - Research dossier for a new future
The Maldives is at an economic and social turning point. As a small island nation with extreme geographical dispersion and high vulnerability to climate change, the country offers a fascinating case study for testing alternative economic systems such as Gradido. This comprehensive research dossier analyzes the current challenges and opportunities facing Maldivian society and assesses the potential for the introduction of a common good-oriented monetary system.
Current economic, social and political situation
Economic upturn with structural weaknesses
The Maldives is currently experiencing a phase of economic growth with projected 5.7% to 6.4% growth for 2025. This positive development is mainly driven by the robust tourism sector, which is expected to grow by over 2.05 million visitors reached a new record. The opening of the new terminal at Velana International Airport is expected to be an important growth driver.mmtv+4
However, there are also structural vulnerabilities: The Inflation rose to 5.6% in April 2025while government debt remains at a worrying level. 134.2% of GDP lie. Tourism, although flourishing, shows declining expenditure per tourist, which calls into question the sustainability of the current growth model.documents1.worldbank+1
Political instability and democratic challenges
Since the change of government in 2023 under President Mohamed Muizzu, the country has been going through a phase of political upheaval. The Press freedom deterioratedThe country fell six places in the Press Freedom Index to 106th place out of 180 countries. Particularly problematic are the ongoing restrictions on freedom of assembly and the government's announcement that the Reintroduce the death penalty.corporatemaldives+1
The high costs of political campaigns represent a further hurdle to democratic participation. On average, candidates must 40-100 workplaces per constituency, resulting in a "maintenance cost" of hundreds of thousands of Rufiyaa per elected candidate.databankfiles.worldbank
Poverty and inequality: the two-tier society
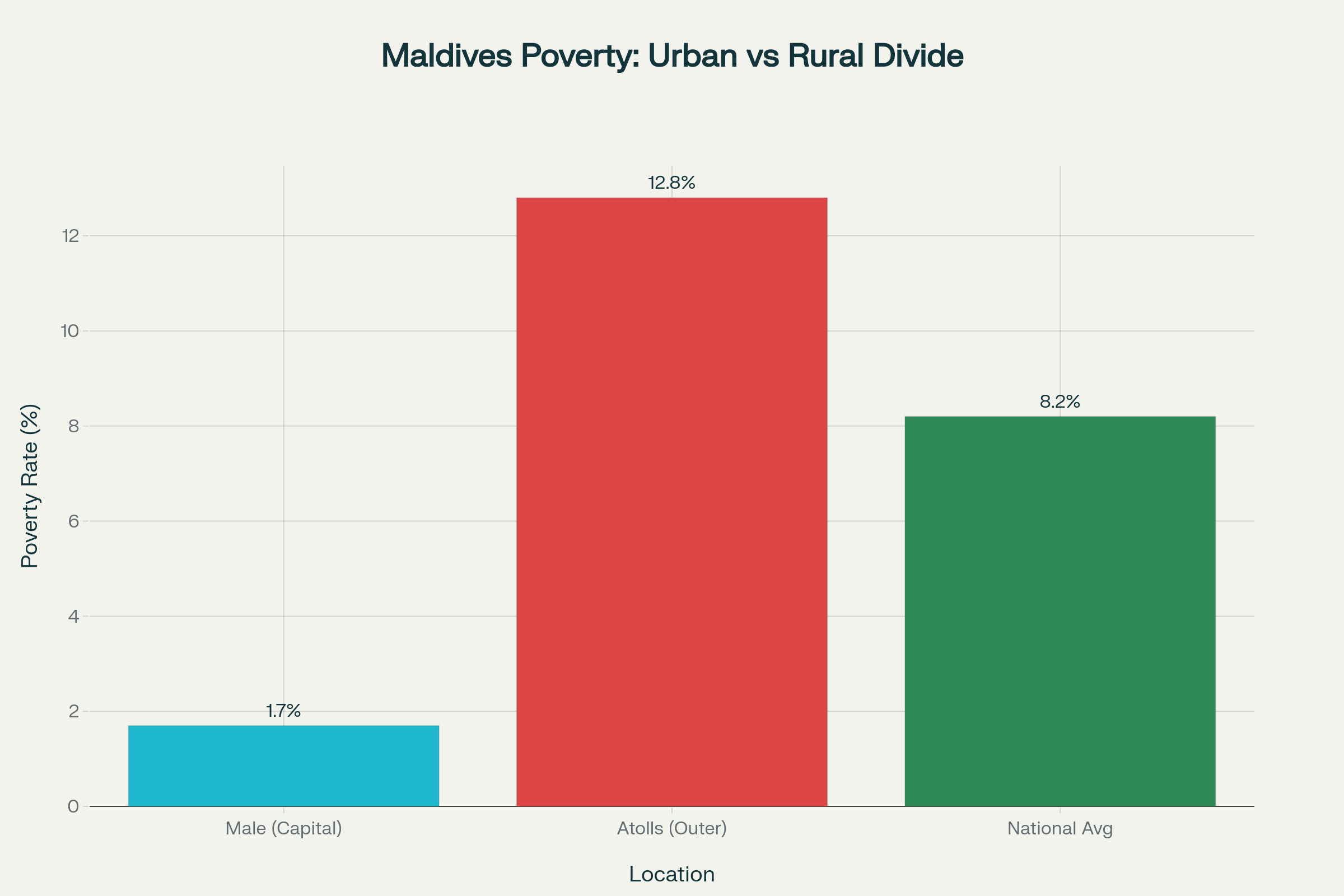
Dramatic differences between Malé and the atolls
The distribution of poverty and inequality in the Maldives reveals a Extreme geographical disparity. While in the capital Malé only 1.7% of the population live below the poverty line, in the outer atolls it is 12,8%. Particularly alarming: 93% of all poor people live in the atollsalthough they only account for around 58% of the total population.openknowledge.worldbank
The average monthly per capita income in Malé is around 7,400 MVRwhile in the atolls with only 4,400 MVR lies. This inequality is also reflected in the Gini index While Malé (25.2) and the atolls (24.2) are relatively equal internally, the national Gini index rises to 29.3, highlighting the gap between the regions.openknowledge.worldbank+1
Structural causes of inequality
The geographical dispersion of the Maldives over 1,196 islands with only 200 inhabited islands creates natural barriers to even development. While Malé, as the traditional seat of the elite, is home to concentrated political and economic power, the outer island communities often function as self-contained economic units with limited access to resources and opportunities.statisticsmaldives+2
Labor migration and social consequences
Massive dependence on foreign labor
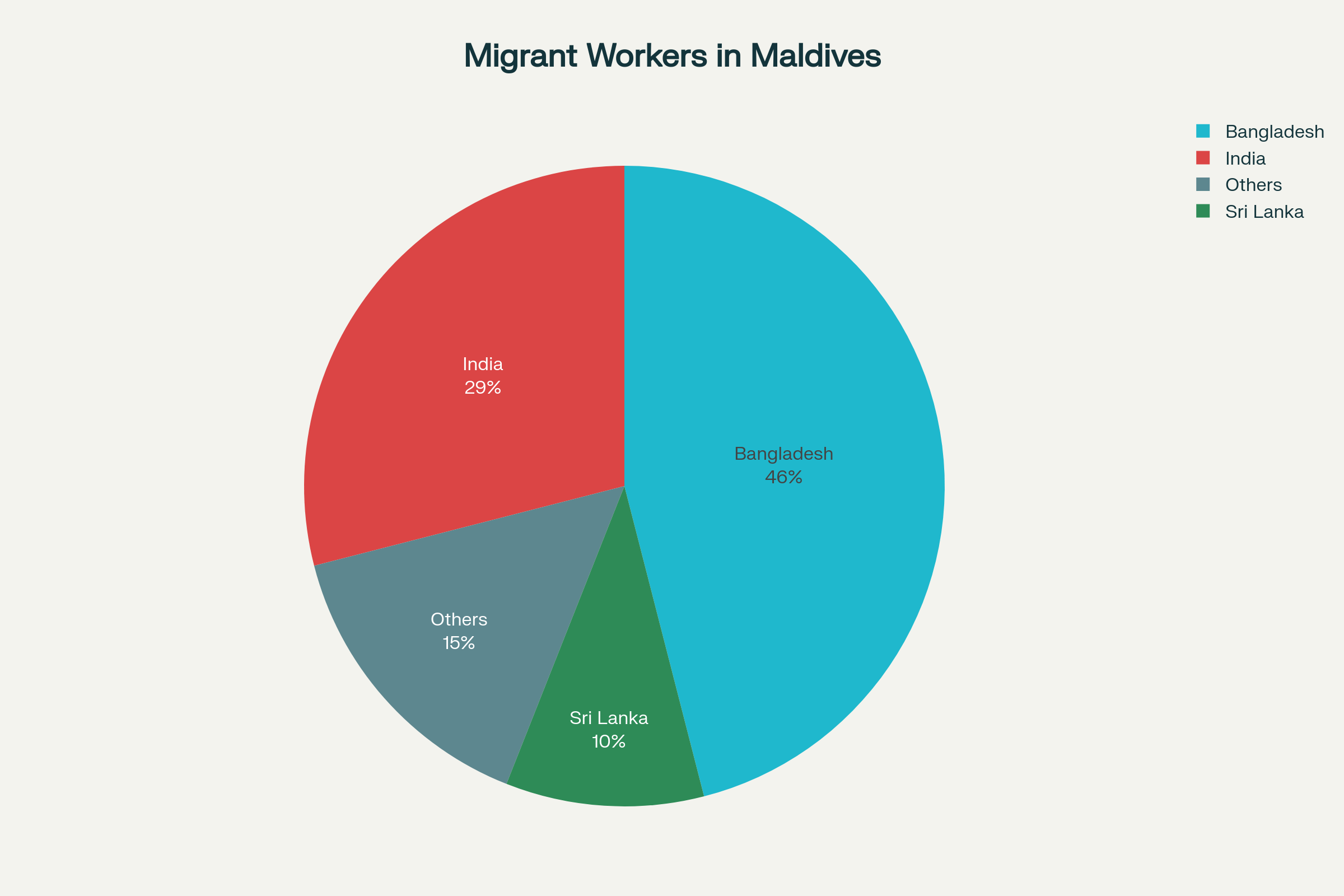
The Maldivian economy is heavily dependent on foreign labor forcewhich are about 32% of the working-age population account for. Of the approximately 130,000 guest workers originate 46% from Bangladesh, 29% from India and 10% from Sri Lanka. These workers are mainly concentrated in Key sectors72% in tourism, 88% in construction and 78% in municipal services.andp+1
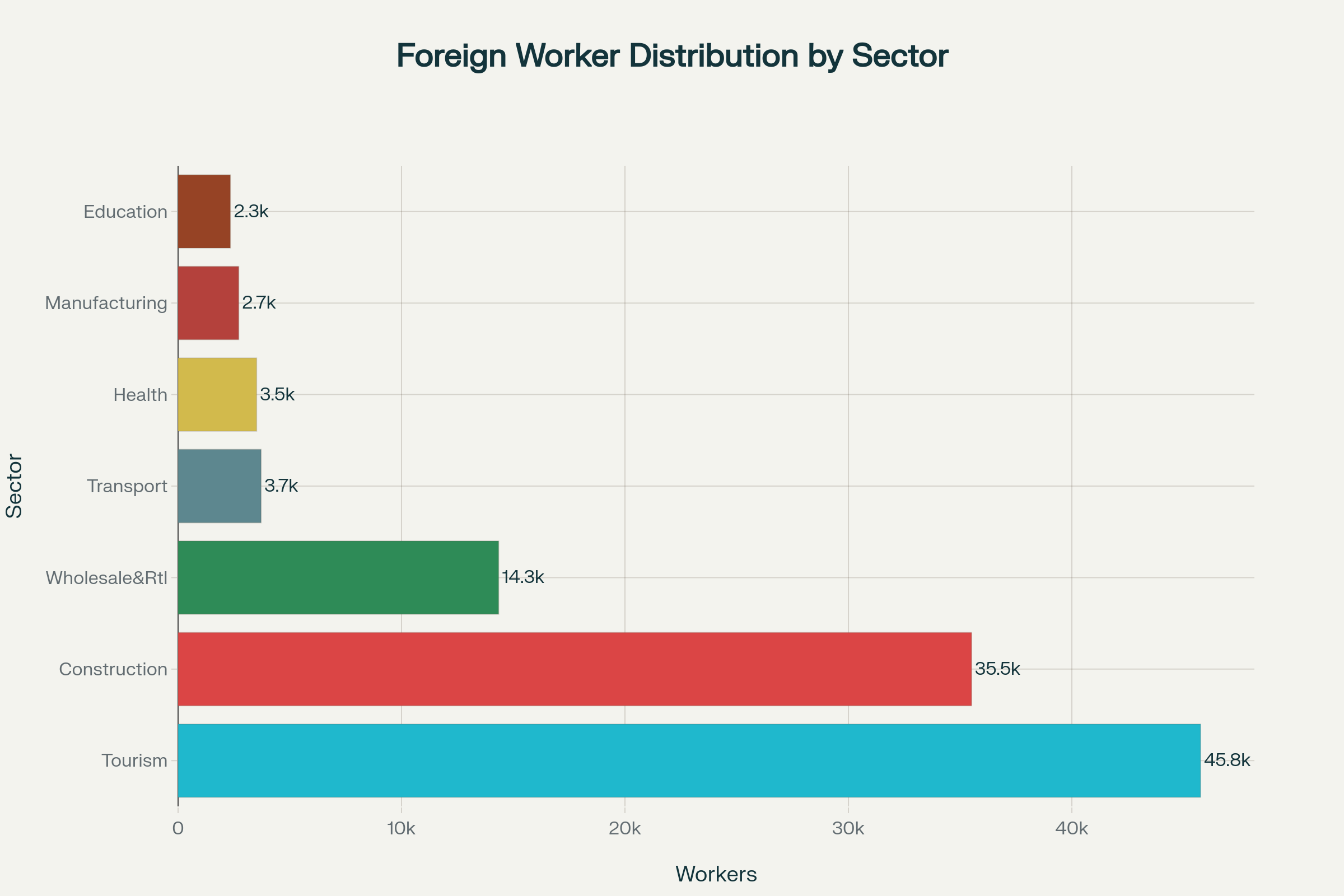
Problematic recruitment practices
The labor migration system is characterized by structural problems coined. Guest workers often pay between 400 and 2,000 USD to recruitment agencies for job commitments. Many have to Pledging family propertyto pay these fees, leading them into a vicious circle of debt and dependency.andp
Of particular concern are reports of Human trafficking and the systematic Withholding of passports by employers. Local recruitment agencies receive 5,000 to 10,000 MVR per worker placedwhich creates incentives for exploitative practices.andp
Impact on the local population
Mass labor migration has far-reaching social consequences. Only One third of employees on resort islands are Maldivianswhich leads to a Decoupling the local population from the fruits of tourism. At the same time Parallel societiesas foreign workers often live in isolation and have little contact with the local population.hrw
Corruption and organized crime
Systemic corruption weakens the state

Corruption remains a serious problem in the Maldives, with 72% of respondents observing an increase in corruption in the country. The Maldivian Anti-Corruption Commission does not have sufficient powers to investigate private corruption. Parliamentarians, ministers and judges were involved in corruption cases that were Losses in the millions for the state caused.amnesty+1
Organized crime and mafia-like structures
Mafia-like groups are becoming a growing problem, with gangs in Drug smuggling, human trafficking and money laundering are involved. These groups have links to Pakistani and Iranian supply networks and exert pressure on the freedom of the press.amnesty
The strategic location of the Maldives along important Shipping routes makes the country particularly vulnerable to transnational organized crimein particular the trade in opium and heroin from Asia's illegal opium-growing regions.amnesty
Cultural strengths and community structures
Family as a cornerstone of society
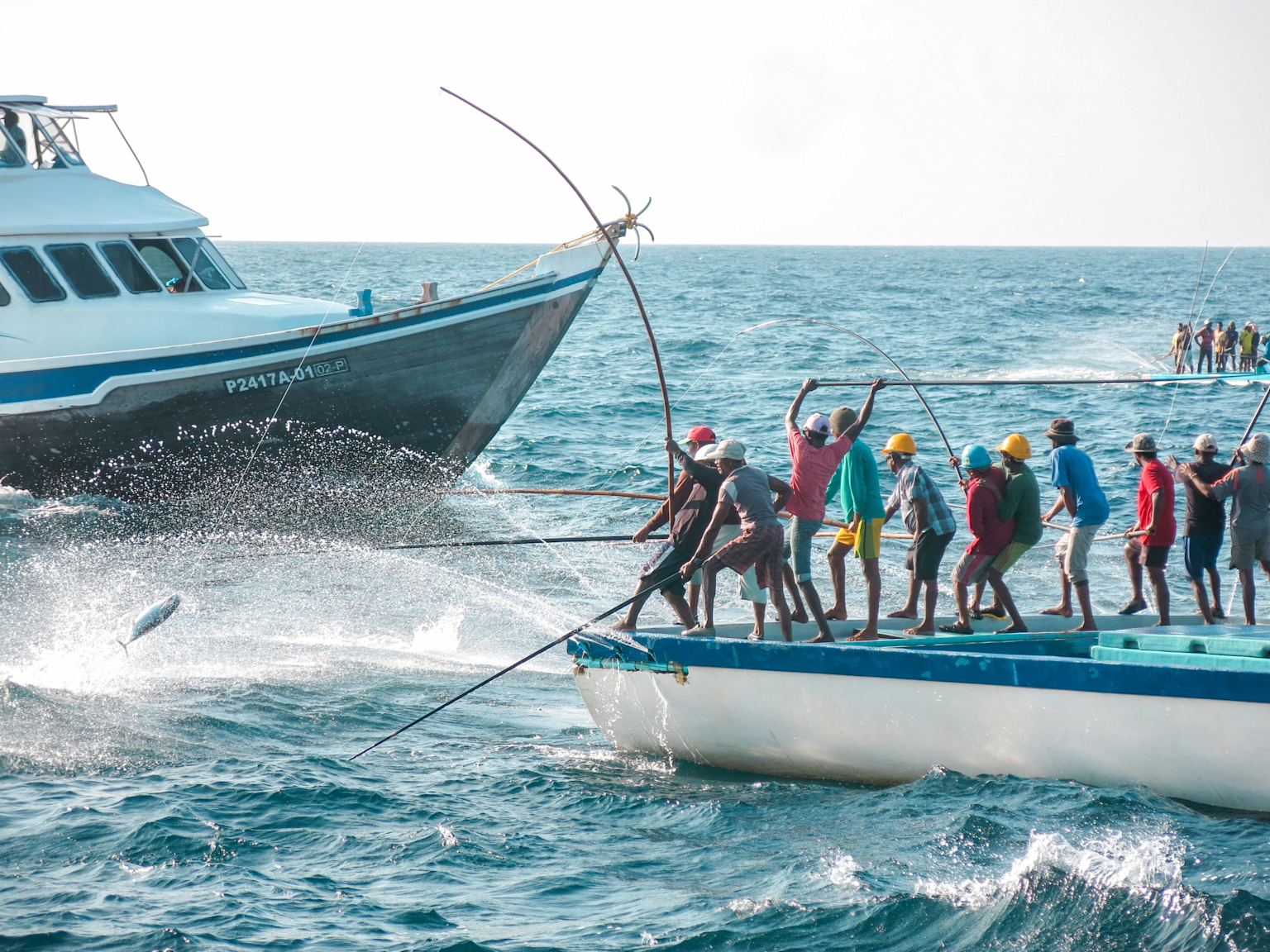

Strong community structures on the islands
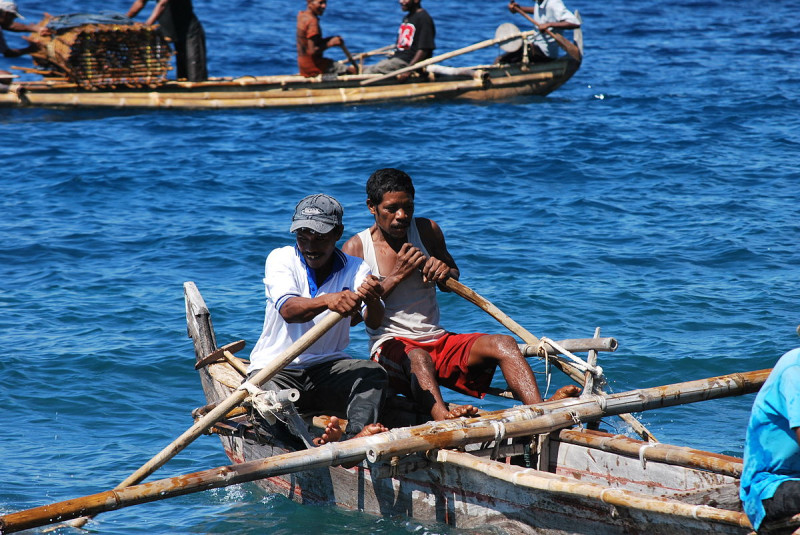

The Island communities outside Malé often form self-contained economic unitswho are related to each other by marriage and Small, close-knit groups whose main economic activity is fishing. The concept of "Island family" extends beyond blood relations, with closely linked communitiesin which neighbors play important roles in raising children and in support networks.wfd+1
Islam as a unifying cultural framework
The Islam has been central since the 12th century for Maldivian identity and daily life. The constitution requires all citizens to be Muslim, and Islamic principles influence many aspects of Maldivian culture, from the five daily prayer times up to dietary rules, modest dress codes and social customs.worldbank
Traditional arts and crafts
Lacquer work (Liyelaa Jehun) are one of the most characteristic traditional art forms of the Maldives, particularly associated with the island of Thulhaadhoo in the Baa Atoll are connected. This intricate art form involves applying colored lacquer to wooden objects in intricate patterns.worldbank
Education and training situation
Successful basic education, but challenges at secondary level
The Maldives has achieved remarkable success in the universal basic education achieved. The Net enrollment rate in elementary school is 96% with high gender parity. For lower secondary level, the net enrolment rate is around 90,5%although there are already gender differences here.transparency
Dramatic decline in the upper secondary level
A serious problem can be seen in the upper secondary levelwhere the net enrollment rate is only 45% falls. This is significantly lower than in comparable small island states and means that more than 80% of students enter the workforce without specialized skills.transparency+1
Innovative solutions: Satellite imaging and geospatial data

In order to overcome the geographical challenges, the government has 2022 the Satellite School Initiative started. This connects remote schools via High-speed Internet with a central hub in Malé, with each satellite school connected to Two facilitator-teachers on site is equipped.medoment+1
The use of Geospatial data for educational planning has opened up new possibilities. Through the mapping of Population density, school locations and transportation infrastructure education planners were able to identify underserved areas and Minimum criterion of 10 pupils for higher secondary levels lower.presidency+1
Healthcare system and social security
Progress in healthcare infrastructure
The Maldives have Significant progress in the healthcare sector and transformed itself from a country with only one hospital in the late 1970s into a country with improved medical infrastructure developed. All inhabited islands have a primary health centerand secondary referral centers are located in inhabited atolls.statisticsmaldives+1
The challenges of geographical dispersion
The Providing equitable healthcare on remote islands remains a critical challenge. Many local islands do not have the economic capacity to attract development, resulting in Migration from these places in search of better jobs, education and healthcare.statisticsmaldives
Innovative telemedicine approaches
The pandemic has increased the importance of Telemedicine which has been successfully used to Bridging barriers to access to healthcare. The recent introduction of Point-of-care machines on 76 islands marks a significant milestone in the expansion of access to healthcare.statisticsmaldives+1
Care work and volunteering
High value placed on unpaid work
Care work and volunteering play a central role in Maldivian society, but are often not adequately recognized or supported. Women traditionally take on Household management and raising a familywhile the concept of Neighborhood help extends through the entire island community.worldbank+1
Potential for gradido integration
The existing system of mutual support and Community aid in the island communities provides an ideal starting point for the implementation of a system such as Gradido, which Voluntary commitment and Contributions to the common good with Gratitude points remunerated.hrcm+1
Openness to innovation and alternative economic models
Ambitious digitization plans
The Maldives show remarkable Openness to technological innovation. The most ambitious project is the planned $9 billion cryptocurrency and blockchain hub in collaboration with MBS Global Investments. This project is to be completed by 2030 16,000 jobs and the country as a regional financial center establish.mmtv+2
Existing digital infrastructure
The Maldives already has a High Internet penetration and Significant growth in digital payments. The development of digital wallets and fintech solutions is actively promoted, which creates a favorable basis for alternative currency systems such as Gradido.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Sustainability as a priority
The Commitment to 100% renewable energy at the planned crypto hub shows readiness, combine innovative technologies with environmental protection. This corresponds to the basic principles of Gradido, which Sustainability and harmony with nature emphasized.hrcm+2
Existing alternative economic approaches
Community-based initiatives in agriculture
Several islands already have cooperative agricultural initiatives. Island councils have allocated additional land for household farmingboth the Subsistence as well as income generation through local markets or connections to resort islands.unesco
Local barter systems and neighborhood help
The traditional Neighborhood assistance systems in the island communities already function as informal exchange networks. These could be used as Prototype for Gradido-based systems in which Services and support with Gratitude points be remunerated.worldbank+1
Agricultural situation and food sovereignty
Extreme dependence on imports

Import the Maldives over 90% of their total food supplywhere India as the main source for staple foods such as rice, flour and sugar. This extreme dependence makes the country Highly susceptible to external shocksas the COVID-19 pandemic has clearly shown.unesco
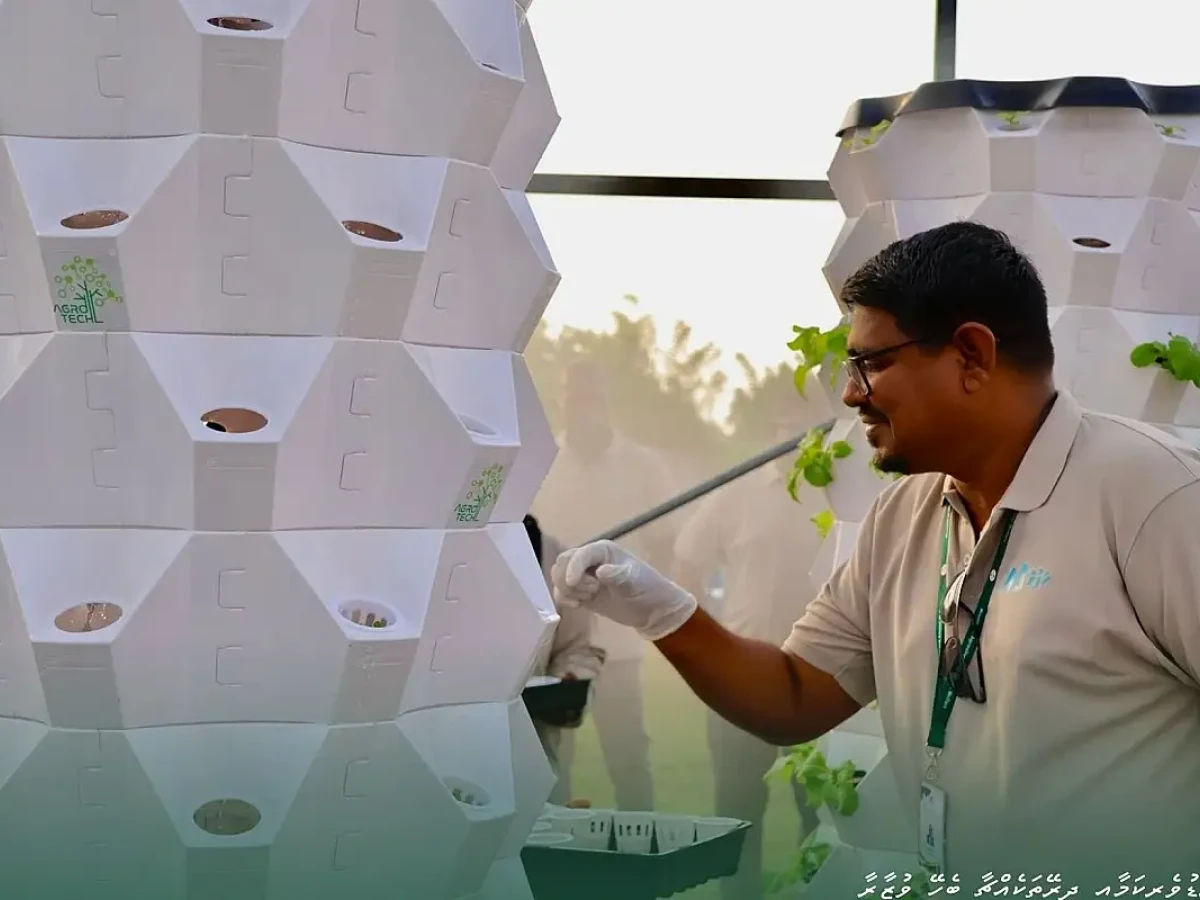
Innovative agricultural approaches
Innovative agricultural methods like Hydroponics, aquaponics and vertical farming are being used more and more frequently. The Project for Developing Sustainable Agricultural Economy (PDSAE) with Japanese support promotes Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) and the development of Soil testing and plant cell culture laboratories.unesco+2
Three categories of agriculture
The Substantial agriculture in the Maldives can be divided into three categories:
Backyard nursery on almost all inhabited outer islands
Designated cultivation areas on inhabited islands beyond the settlements
Uninhabited islands for agricultural purposes – 52 islands are designated for this purpose until 2022globalpartnership
International actors and development cooperation
UN system and multilateral cooperation

The UN system in the Maldives includes 14 Agencieswhich are UN Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework (2022-2026) contribute. The three strategic priorities are:ocindex+1
Shared prosperity and inclusive human development
Sustainable and climate-resilient environment
Gender-sensitive, rights-based and accountable governanceocindex
Development finance and INFF
The Maldives Integrated National Financing Framework (INFF) offers a Comprehensive financing strategy for climate protection. It aims to, both domestic and external resources from the private sector, international financial institutions and philanthropic sources.maldivestour
Potential for Gradido pilot projects
The existing International cooperation structure and the Commitment to innovative financing mechanisms create favorable conditions for the Testing alternative currency systems like Gradido as Supplementary source of funding for development projects.
Potentials and hurdles for Gradido introduction
Greatest potential
1. existing community structures: The traditional closely linked island communities with established Neighborhood assistance systems provide an ideal basis for Community-based monetary systems.worldbank+1
2 Geographical isolation as an advantage: The Natural demarcation of the island communities could Controlled pilot projects without destabilizing the national monetary system.
3. high digital readiness: The Advanced digitization and Openness for blockchain technologies create technical prerequisites for digital gradido implementation.mmtv+1
4. need for diversification: The Economic dependence on tourism and the High import dependency create demand for alternative economic models.census+1
5. care work integration: The existing system of unpaid care work and Volunteering could by Gradido recognition strengthened and made visible.
Main hurdles
1. political instability: The Weak governance and frequent changes of government complicate the Long-term implementation innovative economic systems.corporatemaldives+1
2. corruption and clientelism: Systemic corruption and the Concentration of economic power with a few oligarchs could Resistance to decentralized systems cause.amnesty+1
3. regulatory hurdles: The Strict Islamic jurisdiction and Conservative financial regulation could Legal barriers for alternative currencies.hrw+1
4. educational deficits: The High proportion of unqualified workers and limited financial education the Acceptance of complex currency systems hinder.transparency+1
5. dependence on foreign labor: The Massive presence of foreign workers without Integration mechanisms could be the Coherence of community-based systems undermined.andp+1
Recommended pilot steps
Phase 1: Community-based pilot projects
Selection of 3-5 smaller island communities for initially limited gradido tests
Focus on existing joint projects such as health centers, schools or agricultural cooperatives
Integration with traditional neighborhood support systems
Phase 2: Sector-specific expansion
Piloting in the care sector (elderly care, childcare, community services)
Cooperation with agricultural projects and sustainable tourism initiatives
Integration of educational institutions for awareness-raising
Phase 3: Technological integration
Development of Gradido mobile apps Adapted to local needs
Integration with existing digital infrastructure
Cooperation with the planned crypto hub for technological synergies
Phase 4: Institutional anchoring
Cooperation with island councils for local governance integration
Cooperation with UN development programs
Development of legal framework conditions for complementary currencies
Conclusion and recommendations for action
The Maldives are at a critical juncture social and economic turning point. The extreme Geographical fragmentation, High inequality between urban and rural areas, Massive dependence on guest workers and Structural economic risks create both Urgent challenges as well as Unique opportunities for innovative solutions.
Gradido as a transformative solution
The Gradido system of economic bionics could address several central problems of Maldivian society:
Strengthening the island communities: Through Recognition and remuneration of community work Gradido could use the traditional social structures strengthen and young people perspectives in their home communities instead of forcing them to migrate to Malé.
Integration of the care economy: The Systematic recognition of care work through Gradido could Gender-specific inequalities reduce and Women's economic participation enable.
Sustainable development: The Gradido's natural decay system corresponds to the ecological cycles and could sustainable business practices which are essential for a climate-vulnerable country like the Maldives.
Reduction of import dependency: Through Strengthening local economic cycles and Promotion of regional self-sufficiency Gradido could become Food sovereignty contribute.
Critical success factors
The success of a Gradido implementation depends on several critical factors:
1. political stability: One Long-term political support is essential for the sustainable development alternative economic systems.
2. education and awareness-raising: Comprehensive educational programs the Basic principles of Gradido explain and Trust in the system build up.
3. technological integration: The Existing digital infrastructure must extended in a user-friendly way in order to also less technology-savvy population groups to reach.
4. international cooperation: Partnershipsᅟwith UN organizations and Development agencies can Technical expertise and Financial support provide.
5. cultural sensitivity: The Implementation must respect Islamic values and Strengthen traditional community structures instead of replacing them.
Recommendation for the Gradido research team
The Maldives offer a exceptionally suitable environment for the Testing and further development of the Gradido system. The combination of geographical isolation, strong community structures, urgent need for reform and Openness to innovation creates ideal conditions for Pioneering pilot projects.
We recommend the prompt development of a detailed implementation strategy in close cooperation with local partners, international development organizations and the Maldivian government. The Maldives could not only benefit from Gradido, but also as a global model for the Transformation to sustainable, public welfare-oriented economic systems serve.
The time is ripe for courageous steps in the direction of a new, more sustainable future - and the Maldives could play a Pioneering role that radiates far beyond the borders of the island state.
- https://en.mmtv.mv/3498
- https://www.freiheit.org/south-asia/political-landscape-maldives-after-change-government
- https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/577881560317134445/pdf/Maldives-Poverty-and-Inequality-in-the-Maldives.pdf
- https://atolltimes.mv/post/business/11258
- https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2024/country-chapters/maldives
- https://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/nbs/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Maldives-Poverty-Assessment-2022-1.pdf
- https://corporatemaldives.com/april-2025-economic-update-moderate-growth-evolving-tourism-trends-and-rising-inflation/
- https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2025/country-chapters/maldives
- https://databankfiles.worldbank.org/public/ddpext_download/poverty/987B9C90-CB9F-4D93-AE8C-750588BF00QA/current/Global_POVEQ_MDV.pdf
- https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/entities/publication/57fb0365-2b75-44c0-9962-cba68da6e93a
- https://www.wfd.org/what-we-do/resources/cost-politics-maldives
- https://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/nbs/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/HIES2016-PovertyInequality_Leaflet.pdf
- https://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/mbs/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/MIEG-Feb-2025.pdf
- https://www.wfd.org/sites/default/files/2025-02/wfd_2025_cost_of_politics_in_the_maldives.pdf
- https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/2022-07/3.%20Maldives%20CCA%20Final.pdf
- https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2025/02/18/pr25037-maldives-imf-staff-completes-2025-article-iv-mission-to-the-maldives
- https://www.amnesty.org/en/location/asia-and-the-pacific/south-asia/maldives/report-maldives/
- https://borgenproject.org/the-impact-of-poverty-in-the-maldives/
- https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/maldives/publication/maldives-development-update-2025
- https://www.congress.gov/crs-product/IF12677
- https://transparency.mv/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Maldives-Migrant-Worker-System-Asessment-1-1.pdf
- https://mro.massey.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/10179/3764/02_whole.pdf
- https://medoment.com/how-telemedicine-is-changing-healthcare-in-the-maldives/
- https://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/mbs/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/ILD-2024.pdf
- https://presidency.gov.mv/Press/Article/26173
- https://en.mmtv.mv/3073
- https://maldives.un.org/en/294562-charting-safer-journey-maldives-commitment-migration-governance
- https://www.gpekix.org/blog/how-geospatial-data-transforming-education-remote-maldivian-islands
- https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/integrating-ncd-diagnosis-into-remote-primary-care-in-the-maldives
- https://hrcm.org.mv/en/bidheyseenge-haqquthah
- https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/889841625048965345/pdf/Early-Learning-and-General-Education-in-the-Maldives-Performance-Challenges-and-Policy-Options.pdf
- https://en.mmtv.mv/2926
- https://census.gov.mv/2022/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Migration-Census-2022.pdf
- https://www.eenet.org.uk/blog-how-geospatial-data-is-transforming-education-in-remote-maldivian-islands/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12039589/
- https://maldives.unfpa.org/en/thevelipanel
- https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/unesco-partners-maldives-review-its-national-ict-education-master-plan-digital-transformation-and
- https://investmaldives.gov.mv/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/18.-Healthcare.pdf
- https://www.immigration.gov.mv/work-visa/
- https://www.globalpartnership.org/where-we-work/maldives
- https://ocindex.net/country/maldives
- https://maldivestour.guide/articles/maldives-culture.html
- https://www.undp.org/maldives/projects/project-developing-sustainable-agricultural-economy-pdsae-increase-food-security
- https://anfrel.org/maldives-remains-at-the-same-position-on-the-corruption-perceptions-index-2022-rankings/
- https://yanaa.travel/maldivian-culture-a-journey-through-tradition/
- https://www.undp.org/maldives/news/strengthening-food-security-and-agri-business-maldives
- https://www.icwa.in/show_content.php?lang=1&level=3&ls_id=1813&lid=817
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caste_system_in_the_Maldives
- https://sdg.iisd.org/commentary/guest-articles/exploring-climate-change-impacts-on-food-security-in-maldives/
- https://www.unodc.org/documents/Maritime_crime/UNODC_GMCP_Organised_Crime_Networks_Linked_with_Drug_Trafficking_in_the_Eastern_Indian_Ocean_Region.pdf
- https://vermillionmaldives.com/society.htm
- https://investmaldives.gov.mv/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/12.-Enhancing-Food-Security-in-the-Maldives.pdf
- https://transparency.mv/files/media/6dca8a9f7beda482335bb654b88020f7.pdf
- https://countrystudies.us/maldives/6.htm
- https://mnu.edu.mv/climate-resilient-agriculture-for-food-security-in-maldives/
- https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2018/9/18/report-exposes-maldives-orgy-of-corruption-ahead-of-election
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Culture_of_the_Maldives
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/sustainable-food-systems/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2024.1444269/full
- https://www.unodc.org/roseap/uploads/documents/2024/TOCTA_Pacific_2024.pdf
- https://www.travelescapesmaldives.com/Blogs_details/the_culture_and_traditions_of_the_maldives_exploring_the_local_way_of_life
- https://gradido.net/de/
- https://news.bit2me.com/en/Maldives–a-financial-center-with-a-star-asset–Bitcoin
- https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/2022-07/UNSDCF%20Final%20for%20Website%20(111021).pdf
- https://wirundjetzt.org/gradido-die-natuerliche-oekonomie-des-lebens/
- https://cryptodnes.bg/en/maldives-unveils-9b-crypto-hub-plan-to-transform-island-economy/
- https://maldives.un.org/en
- https://www.michael-zorn.at/zum-nachlesen-hoeren/geld-zum-wohle-aller-teil-4-gradido-natuerliche-oekonomie-des-lebens/
- https://coincrowd.com/blogs/maldives-to-build-9-billion-crypto-hub-to-attract-investment
- https://www.undp.org/maldives
- https://wirundjetzt.org/wirtschaft-und-geld/
- https://plasbit.com/crypto-debit-card-maldives
- https://www.developmentaid.org/donors/view/112773/undp
- https://gradido.net/de/gradido-eine-oekonomie-der-dankbarkeit/
- https://www.urbantechex.com/fintech
- https://www.dfat.gov.au/about-us/publications/development-cooperation-fact-sheets-for-country-regional-and-sector-thematic-programs/maldives
- https://society4th.org/project/gradido/
- https://cryptodnes.bg/en/best-crypto-to-buy-now-as-maldives-unveils-a-9-billion-blockchain-paradise/
- https://foreign.gov.mv/index.php/en/multilateral/international-organisations/other-organisations
- https://gradido.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/gradido-ebook-de.pdf
- https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/099060624144515101/pdf/P18010018ba7020fc1bd1b12ee8ea7e80dc.pdf
